Titration of phosphoric acid with sodium hydroxide
general remarks
Titration of the phosphoric acid H3PO4 is an interesting case. Although often listed together with strong mineral acids (hydrochloric, nitric and sulfuric) phosphoric acid is relatively weak, with pKa1=2.15, pKa2=7.20 and pKa3=12.35. That means titration curve contains only two inflection points and phosphoric acid can be titrated either as a monoprotic acid or as a diprotic acid. In the first case acid has to be titrated against indicator changing color around pH 4.7 (for example methyl orange), in the second case - against indicator changing color around pH 9.6 (for example thymolphthalein). Phenolphthalein can't be used, as it starts to change color around pH 8.2, when phosphoric acid is titrated in about 95%.
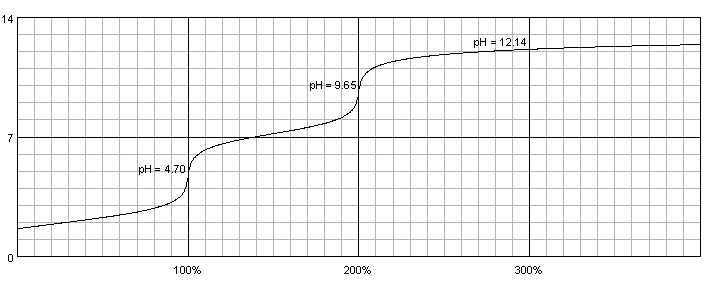
0.1M solution of phosphoric acid titrated with 0.1M solution of strong base. pKa1=2.15, pKa2=7.20, pKa3=12.35. Titration curve calculated with BATE - pH calculator.
It is interesting to mention, that phosphoric acid can be titrated as triprotic - if PO43- anion is precipitated first using metal ions (for example Ca2+ or Ag+):
2H3PO4 + 3CaCl2 → Ca3(PO4)2 + 6HCl
After precipitation HCl can be titrated against phenolphthalein.
reaction
Depending on the indicator used reaction taking place is either:
H3PO4 + NaOH → NaH2PO4 + H2O
or
H3PO4 + 2NaOH → Na2HPO4 + 2H2O
sample size
Assuming 50 mL burette, aliquot taken for titration should contain about:
| indicator name | titrant concentration | mass H3PO4 | moles H3PO4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| methyl orange | 0.1 M | 0.34-0.44 g | 3.5-4.5 mmol |
| 0.2 M | 0.69-0.88 g | 7.0-9.0 mmol | |
| thymolphthalein | 0.1 M | 0.17-0.22 g | 1.7-2.3 mmol |
| 0.2 M | 0.34-0.44 g | 3.5-4.5 mmol |
end point detection
As explained above, during titration of phosphoric acid we can use either methyl orange and detect first end point around pH 4.7, or thymolphthalein and detect second end point around pH 9.6. Decision which indicator should be used can be based on the approximate concentration of phosphoric acid and titrant and on personal preferences - some find it easier to detect change of the methyl orange color than the appearance of a blue hue of thymolphthalein.
solutions used
To perform titration we will need titrant - 0.2 M or 0.1 M sodium hydroxide solution, indicator - methyl orange or thymolphthalein, and some amount of distilled water to dilute hydrochloric acid sample.
procedure
- Pipette aliquot of phosphoric acid solution into 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask.
- Dilute with distilled water to about 100 mL.
- Add 2-3 drops of methyl orange or 3-4 drops of thymolphthalein solution.
- Titrate with NaOH solution till the first color change.
result calculation
Depending on the indicator used reaction is either
H3PO4 + NaOH → NaH2PO4 + H2O
or
H3PO4 + 2NaOH → Na2HPO4 + 2H2O
and stoichiometric ratio of sodium hydroxide and phosphoric acid is either 1:1 or 2:1.
To calculate phosphoric acid solution concentration use EBAS - stoichiometry calculator.
In the case of titration against methyl orange download determination of phosphoric acid as monoprotic reaction file, open it with the free trial version of the stoichiometry calculator.
In the case of titration against thymolphthalein download determination of phosphoric acid as diprotic reaction file, open it with the free trial version of the stoichiometry calculator.
Click button above NaOH in the input frame, enter volume and concentration of the titrant used. Click button. Read number of moles and mass of phosphoric acid in the titrated sample in the output frame. Click button in the output frame below phosphoric acid, enter volume of the pipetted sample, read phosphoric acid concentration.
sources of errors
As usual, when titrating with sodium hydroxide, we should pay special attention to its concentration. Strong base solutions are not stable as they tend to absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide. In the case of phosphoric acid we should additionally be very carefull about end point detection, as steep parts of the titration curve are in both cases relatively short. As usual, there are also general sources of titration errors.



